a drug gets eliminated by either ZERO ELIMINATION CONSTANT or FIRST ORDER ELIMINATION.
a zero order elimination is when the plasma concentration of a drug decreases linearly with time:
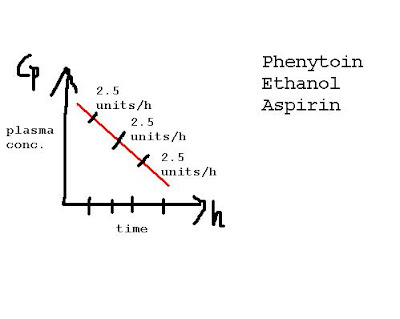
a drug with first order elimination has a rate of elimination proportional to the drug concentration:

from the graph you can see, the more drug in the system (the higher the plasma conc.), the faster the drug is eliminated.
drugs are also metabolized in the system propr to elimination. there are 2 phases of this metabolism.
phase I includes reduction, oxidation and hydrolysis. it yields water soluble metabolites. sometimes a drug is activated after phase I metabolism. the cytochrome p450 system is connected to phase I. old patients lose phase I first!
phase II @ conjugation includes acetylation, glucuronidation, sulfation and yields inactive metabolites that are renally excreted.